16
www.techno-isel.com
Technical Information
Plain bearings rarely ever carry more than 3000 psi.
Another way of determining a bearing’s load capacity is through maximum PV factor. This is the value of
pressure on the bearing (psi) times the shaft speed (feet/min).
If the PV value for the application is less than the maximum PV value for the bearing
considered, and if the application pressure load does not exceed the compressive
strength of the bearing material, and if the application speed does not exceed the
maximum permissible speed of the bearing considered, then the bearing considered
may well serve the application.
Ball Bearing Selection: The nature of the application load must be known and compared to the load
carrying capability of the considered bearing. Combination loads should be converted into a single equivalent
radial or thrust load using manufacturer’s equations to size the application requirement. Regarding speed
requirements, tolerance grade, lubrication, retainer design and bearing seal type must be considered, and
the maximum application speed must not exceed the maximum allowable bearing speed. A useful guide for
ball bearing selection is to consider the DN value (speed value) of the bearing. The DN value is the product
of the bore size (mm) and the shaft speed (rpm). This quantity will suggest the type of lubrication and
tolerance grade required. Use for the ball bearing type include applications involving shafts that may be
slightly misaligned.
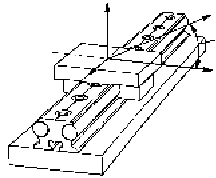
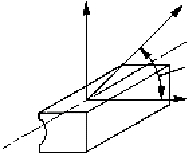
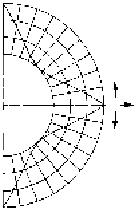
Linear Ball Bearing Selection: This selection is generally based on speed and load requirements.
Understanding the orientation and magnitude of the application loads on the bearing is of paramount
importance. Most manufacturers and suppliers of such bearings will include information regarding the load
capabilities with respect to load orientation, as shown below.
Roller Bearing Selection: Load, speed, and shaft alignment are the most important features to consider
when selecting roller bearings. It is suggested that, in the case of needle bearings, the shaft parallelism be
less than 0.0003" for the entire length of the bearing section. Further, the shaft should be round to within
0.0002" or to within half the shaft tolerance.
FZ
F
A
FY
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
FY
X
FZ
A
F
80°
60°
40°
20°
0°
20°
40°
60°
80°
Force on Single Bearing
Force on Double Bearing
Series 1 Bearings