28
www.techno-isel.com
Technical Information
1
1
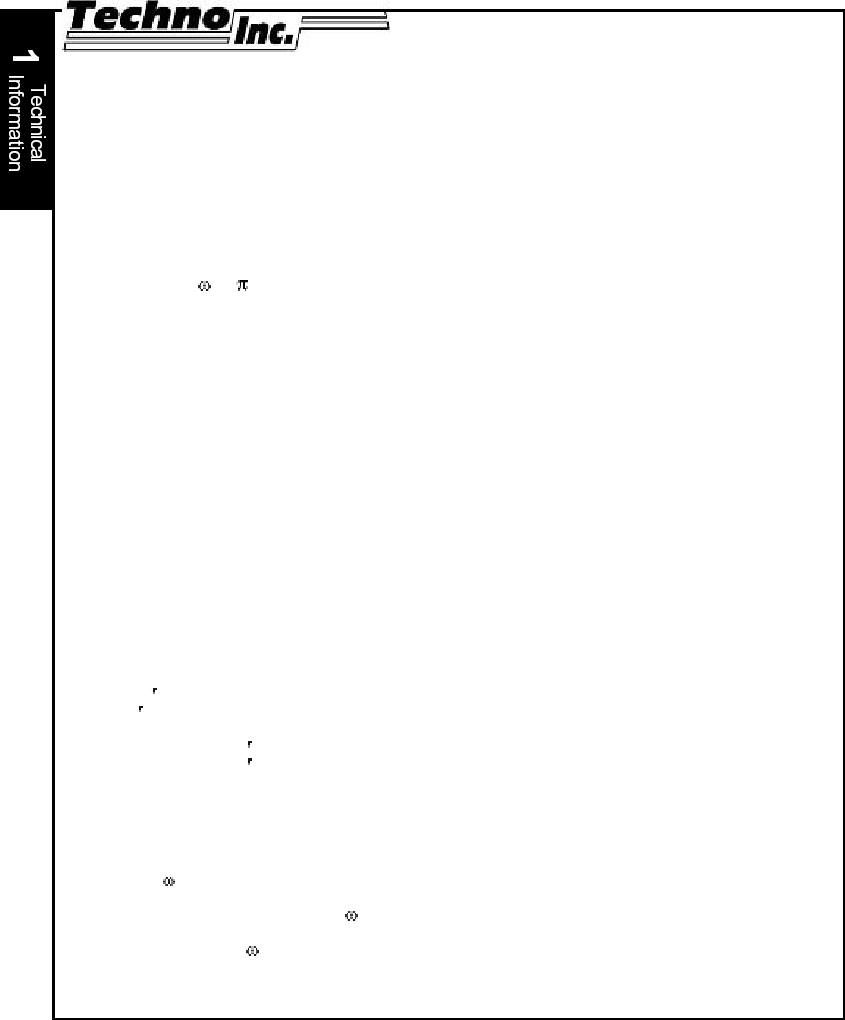
I(eq) = w x ––– x .025 = 1000 x ––– x .025 = 1.0 lb in2
p2 25
I (screw) = D4 x length x .028 = 5.06 x 48 x .028 = 6.8 lb in2
I (rotor) = 2.5 lb in2
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
I (total) = 10.3 lb in2
Velocity is 0.15 feet per second, which is equal to 1800 steps per second (motor steps in 1.8° increments).
Torque to accelerate system:
' x 1.8 1 1800 3.1416 x 1.8 1
T = 2 x IO x ––– x –––––––– x ––– = 2 x 10.3 x ––––– x –––––––––––– x ––– = 484 oz in
t 180 24 0.1 180 24
Torque to overcome friction:
F = .393 x T x p x eff.
6
––––
F
16
T = ––––––––––––– = ––––––––––––– = 0.22 oz in
.393 x p x eff. .393 x 5 x 0.90
where:
F = frictional force (lb)
T = torque (oz·in)
p = lead screw pitch (threads per inch)
Total torque required = 0.22 oz in + 484.00 oz in = 484.22 oz in
After determining the required motor size, it is recommended to add a 20% factor of safety so that unexpected
dynamic loads are easily handled by the motor.
Sizing Servo Motors: Two separate torque figures are needed when selecting a DC motor — a peak
torque, being the sum of acceleration and friction torques, and a continuous torque, which is the friction
component only. The torque produced by the motor is given by:
T = K
I
where K
is the motor torque constant (e.g., Nm/amp) and I is the drive current (amp). The choice of motor
and drive must satisfy the following conditions:
1. The product of K
and peak drive current must give the required peak torque
2. The product of K
and continuous drive current must produce sufficient continuous torque.
3. The maximum allowable motor current must be greater than the peak drive current.
4. At maximum speed and peak current, the voltage developed across the motor must be less than
80% of the drive supply voltage.
The voltage across the motor is given by:
E = KE + R I
where KE is the motor voltage constant, the speed, R the winding resistance (ohms) and I the peak current
(amperes). The speed units should be the same in each case; i.e., if the voltage constant is in volts per
radian per second, then should also be in radians per second.
To make the most efficient use of the drive, the chosen solution should utilize most of the peak drive current
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·